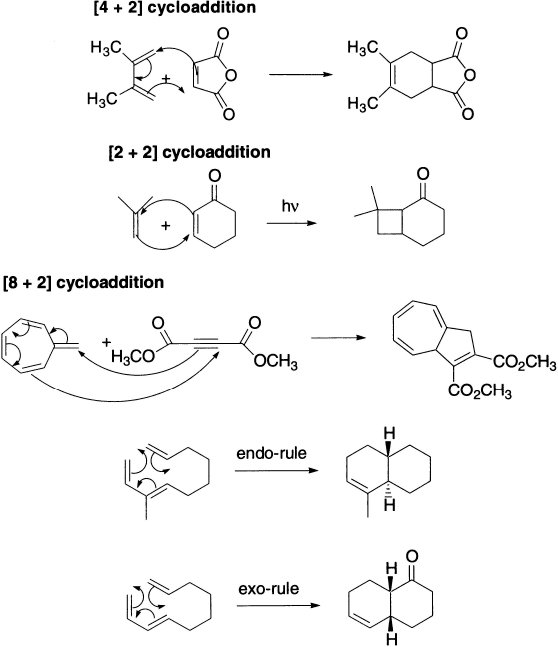
In a cycloaddition reaction, two different π-bond-containing molecules react to form a cyclic molecule. The reverse process is known as cycloreversion or retro-cycloaddition. The Diels-Alder reaction is one of the best known examples of a cycloaddition reaction. Cycloaddition reactions are classified according to the number of π electrons that interact in the reaction. The Diels-Alder reaction is a [4+2] cycloaddition because one reactant has four interacting π electrons and the other reactant has two interacting π electrons. Only the π electrons participating in electron rearrangement are counted. If the number of π electrons in the two components is m and n respectively, the cycloaddition is called [m+n] addition. Cycloaddition may be intermolecular- or intramolecular depending on whether the two components belong to different or the same molecule.
Leave a Reply