The elimination of HX from a vinyl halide produces an alkyne. Very strong bases, such as NaNH2 and LDA are generally used. There are three possible pathways for elimination reactions at sp2 hybridized atoms. The product alkyne has no stereochemical features.
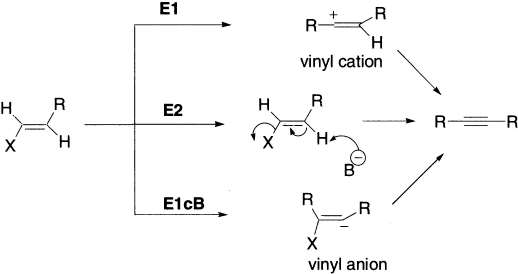
The E1 route is unlikely because the vinyl cation (sp2-hybridized) is very unstable, and energetic considerations favour the concerted E2 and E1cB mechanisms. The E1cB route generates vinyl anion (sp2-hybridized). The lone pair in the hybrid orbital of a vinyl anion is orthogonal to the π system and coplanar with the C-X bond that facilitates the loss of X− in the next step.
An anti-periplanar arrangement of C–Br and C–H is attainable with a vinylic bromide too, provided the Br and H are trans to one another. E2 elimination from the Z isomer of vinyl bromide gives an alkyne rather faster than elimination from the E isomer, because in the E isomer the C–H and C–Br bonds are syn-periplanar.
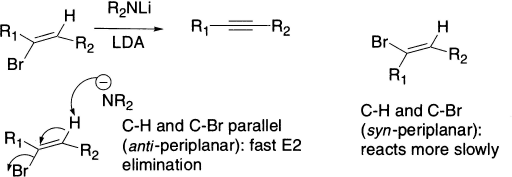
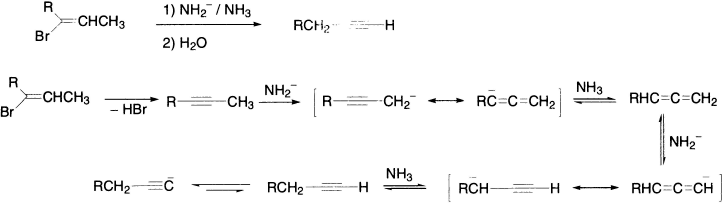
The base used here is LDA (lithium diisopropylamide) made by deprotonating i-Pr2NH with BuLi. LDA is very basic (pKa ~35) but too hindered to be nucleophilic, ideal for promoting E2 elimination. Base-catalyzed elimination from alkenyl derivatives gives usually a terminal alkyne. This is because the first product formed undergoes a series of prototropic shifts, catalyzed by the strong base. The thermodynamic driving force is the stability of the acetylenic anion, which, on the addition of water, gives the terminal alkyne.
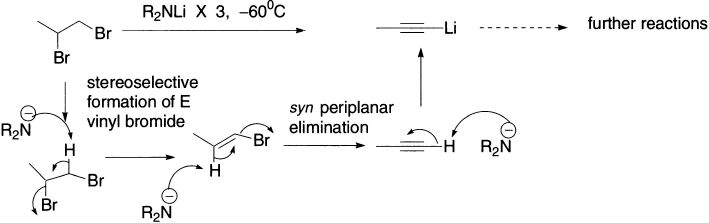
Vinyl bromides can themselves be made by elimination reactions of 1,2-dibromoalkanes. Watch what happens when 1,2-dibromopropane is treated with three equivalents of R2NLi: first, elimination to the vinyl halide; then, elimination of the vinyl halide to the alkyne. The terminal alkyne is acidic enough to be deprotonated by R2NLi, and this is the role of the third equivalent. Overall, the reaction makes a lithiated alkyne (ready for further reactions) from a fully saturated starting material. This may well be the first reaction you have met that makes an alkyne from a starting material that does not already contain a triple bond.
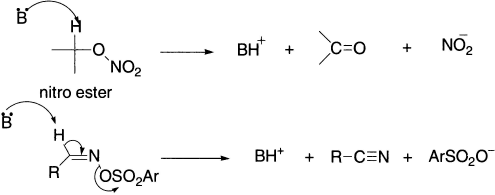
Derivatives of aldoximes in anti geometry undergo base-catalyzed elimination to give nitriles. Examples of eliminations to give C=O bonds and C ≡ N bonds are:
Leave a Reply